AftabRad
Revit Add-in -> Export To Radiance -> Type of Sky/Analysis: View Analysis
(EN 17037)
Visibility calculations show how much of an object can be seen from different points within the model (from Autodesk Ecotect Analysis 2011, Calculation Wizard, Visibility Analysis).
Visibility analysis requires to define one or more objects as interesting landmarks.
Therefore, to do the analysis we should do the following steps.
1- Press calculationPointCreation button in the AftabRad Add-in

2- Select Visibility Analysis in the Type of Sky/Analysis
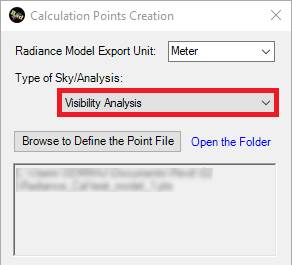
3-
In the Calculation Point Creation page, as you see in the below,
other than other specifications, we need to define which Revit elements can be
defined as landmarks.
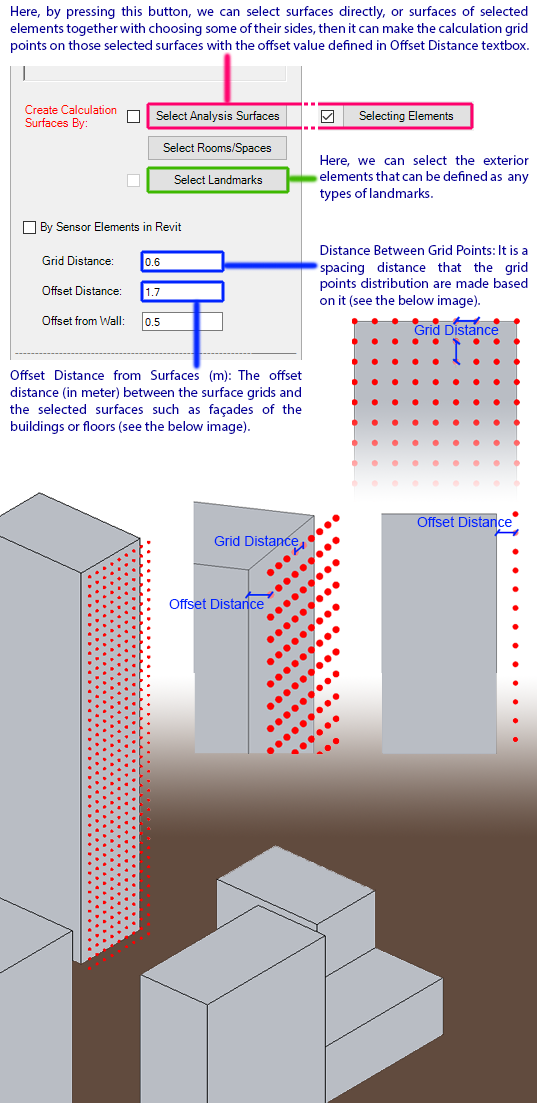
Moreover,
here, we need to create calculation grid point by selecting some surfaces in
the model, some elements together with choosing some of their sides,
or by choosing
some of the rooms/spaces inside the building to do the analysis.
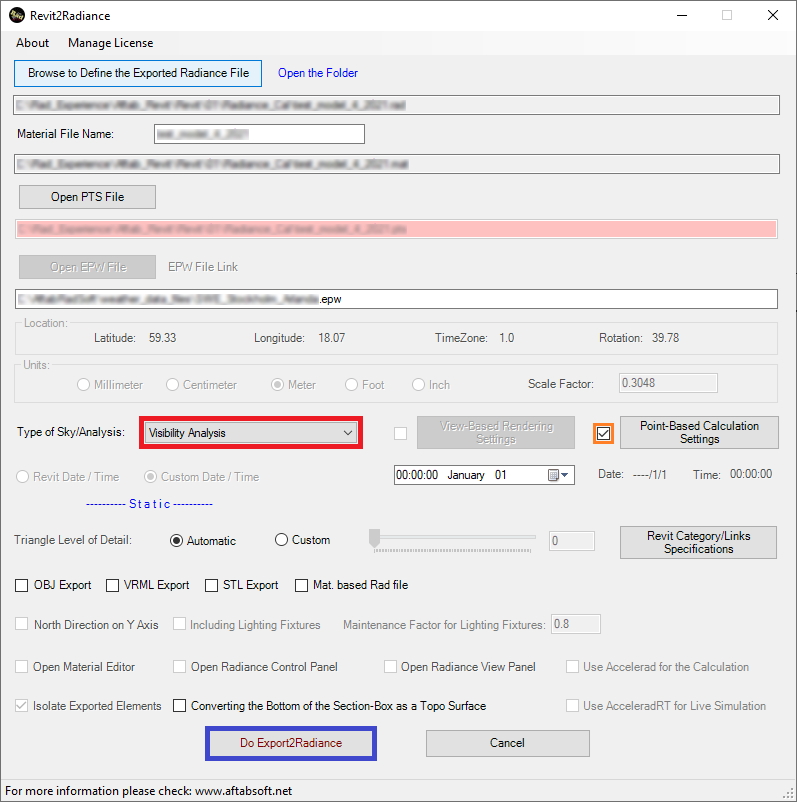
4-
Then, we need to come back to the main Revit2Radiance page, Close
the page, and re-open it.
5-
Check the checkbox next to the Rtrace Settings button, and press
the Do Export2Radiance button.
6-
Then, you need to wait until the calculation is finished.
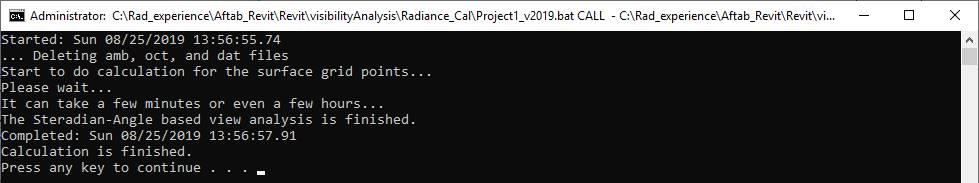
7-
Now, it is time to import the calculation data into Revit. Therefore, the
next step is to press the importToRevit Button.

8-
In the Data2Revit page, press Open Dat File button.
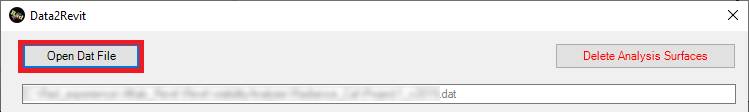
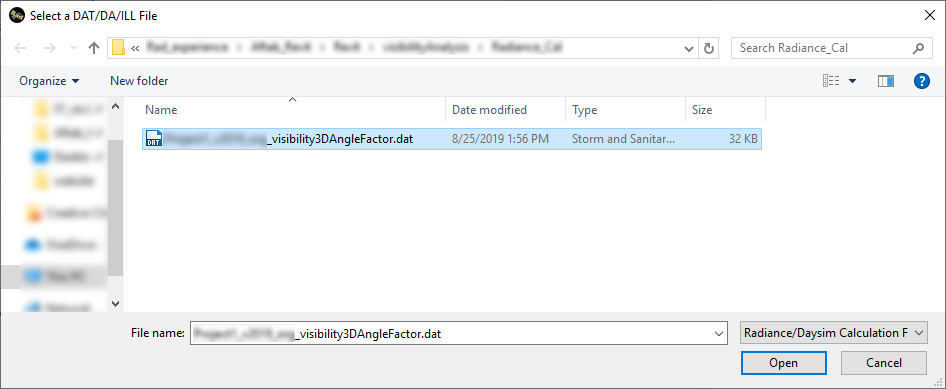
Please select the …_visibility3DAngleFactor.dat
file.
9- When importing the …_visibility3DAngleFactor.dat file, this add-in automatically chooses Custom for Calculation Type. Keep the Custom as the Calculation Type and press Import.
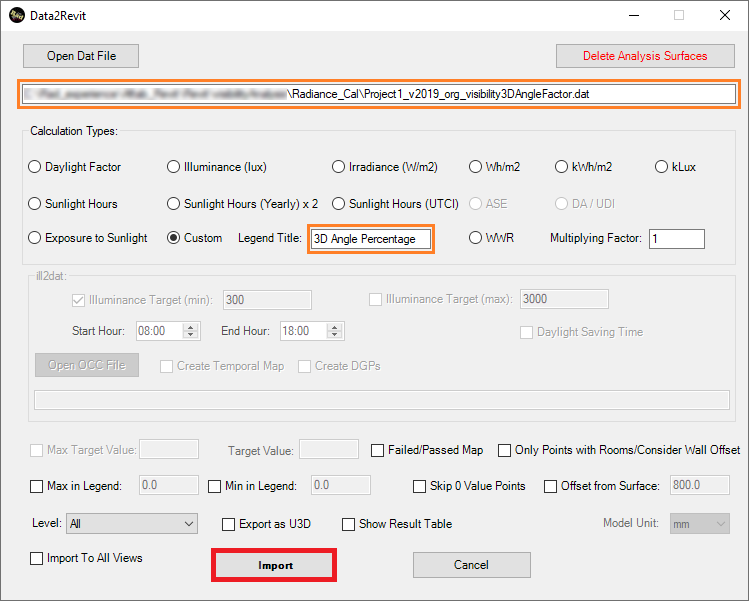
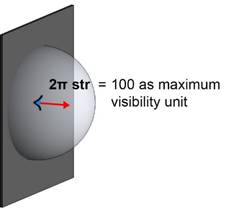
10- Regarding the unit that can be measured in this analysis, here is its definition:
The 3d angle of a sky dome when there is no obstructions and our view is toward zenith of sky is 2π steradian.
If we consider 2π steradian as 100 unit as maximum value (see the image below), the 3D angle value for each point is defined as the cumulative value of all elements that are defined as landmarks and visible from that point.
Its maximum value is 100 when the landmark covers the whole 3D view hemisphere angle. No points can reach 100 unless we define the sky as landmark, our view is upward, and it has no obstructions.
Generally, such values can seldom exceed 50.